How Combining Data Mesh and Data Fabric with Modern MDM Turbocharges Digital Transformation

Getting information into the hands of experts who can drive maximum value from it remains one of the most significant barriers to digital transformation today. It’s an old problem and growing bigger by the minute as the volume of applications and silos expand exponentially. For example, one study predicts that enterprise data will increase at a 42% annualized growth rate in the next two years.
Despite having this information, many organizations are no closer to realizing the data-driven holy grail. Respondents in a recent survey, for example, reported that their organizations are making more “gut instinct” decisions versus just last year.
That’s why there has been much buzz recently around the potential for data “virtualization” to fix these problems. Virtual data includes information architecture concepts such as data mesh and data fabric. Data virtualization approaches do not solve the most significant point of friction most enterprises have, however, which is creating accurate, trustworthy core data in real-time. Combining modern MDM solutions with a virtual approach can unleash the power of data and finally lead any organization into the data-driven promised land.
Data Virtualization Seeks to Solve the Silo Problem
Data silos are growing and creating big challenges for enterprises. Data is also always moving, it’s always morphing. Practitioners transform it, systems transform it, and much of it moves to the cloud, including cloud data warehouses, cloud data lakes, SaaS solutions, platform solutions, or master data management (MDM) solutions like Reltio. There is a secular and massive movement to the cloud as part of a broad trend toward digital transformation. As this march to the cloud continues, however, so too does the proliferation of apps, which collect increasingly more data every single day.
With so many data sources and storage locations, whether on-prem or in the cloud, accessing the data in an organized, structured and usable way remains problematic. Data virtualization seeks to solve that through the seamless delivery of organized, actionable, and reusable data sets from data warehouses, data lakes, SaaS applications and other sources and place it into the hands of the right people for making critical business decisions. Virtual data can help organizations put the correct data into the hands of their experts and allow them to move towards data-led decision-making and give a competitive edge. These approaches seek to deliver fast access to actionable, domain-specific and reusable data products across an entire enterprise landscape to fuel analytics and other data-driven initiatives.
Figure 1 below shows a simple illustration of data sources and data consumers.
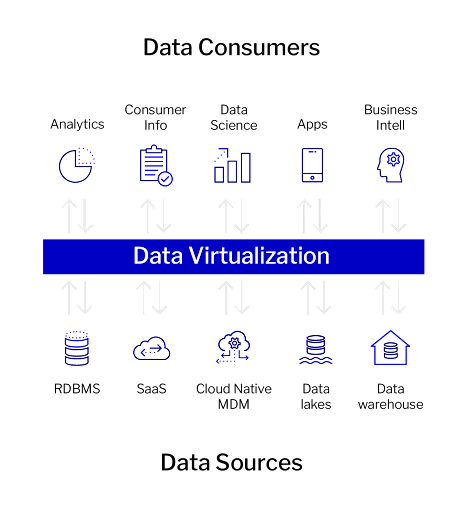
Enterprises are also demanding increasing speed. It’s a competitive advantage for companies to move from raw data to insight to action faster than their competitors. Innovation teams are demanding the ability to experiment faster, especially with machine learning, tweaking models to constantly optimize or feed the growth engine.
This is where data mesh and data fabric help bridge the gap from raw data pools to actionable data. So what are they?
Moving Data into the Hands of Domain Experts
Data lake architecture models have common failure modes that lead to unfulfilled promises at scale. Monolithic, centralized, data often resides outside the organizational domain that needs it. And the teams that manage the data storage and information pipelines aren’t well-versed in organizational domains that require quality, actionable. Data mesh is a concept that moves information from centralized lakes and warehouses and puts it into the hands of domain and subject matter experts. In this construct, data is treated as a product and owned by domain experts. Data fabric is more akin to metadata, it is a catalog system that identifies what information is available. Fabric can help domain experts, and analysts determine where data can be used.
Data mesh and fabric patterns apply to analytics – though fabric is more generic and stretches into operational use cases. Mesh and fabric approaches can be complementary and can be used together to build a mature enterprise-wide data program. Getting data into the hands of the domains that need it will help organizations move toward to promised land of digital transformation. Figure 2 below shows a high-level comparison of data lake/data warehouse and the data mesh and data fabric approaches.
|
MDM: Addressing the Root Cause of Untrustworthy Data
Data virtualization concepts are catching on because the problem it seeks to solve continues to hamstring businesses in every sector – which is getting value from their own data. But organizing, packaging and making data more readily available does not solve the data quality problem most enterprises have. Virtual data moves data through a more efficient pipeline but it doesn’t fix it.
Domain experts and business users not only need access to specific data, but they also need better quality information to make informed decisions. Core data, in particular, is the lifeblood of any enterprise. Core data is information about customers, vendors, locations, assets, and suppliers, among other things i.e. data that every organization runs on – any of the vital information to a specific market segment. The problem organizations have with core data is that it can reside in many different silos. And the core data is often inaccurate, outdated, or duplicated elsewhere.
This is why organizations undergoing digital transformations are frequently frustrated–poor quality core data is slowing them down, so– they spend more time and resources trying to fix those problems than they do gaining insight. Hence the recent trend we’ve seen where data-rich organizations are reverting to “gut instinct” decision-making. It’s easier to trust your gut than it is to trust bad data because you know the data is wrong. Simply migrating to a cloud data warehouse does not make that problem go away.
Clean Connected Data is the Foundation for any Data Architecture
Data Virtualization is here to stay. Data virtualization promises to unlock the value of enterprise data, and deliver on the promise of evolving into a data-driven organization. Mesh and fabric approaches can be complementary and can be combined to build a mature enterprise-wide data program. These concepts will help solve challenges organizations have today and will scale with them as they collect more data and create more silos. Mastered core data, however, remains the foundational element for any virtualized data approach. That’s why we’re seeing MDM evolve from a reluctant to an indispensable spend. Every organization is becoming a data-driven organization, which requires domain expertise and high-quality, actionable information to make sound business decisions, satisfy its customers, and create more enterprise value.
