What is True Cloud-Native Master Data Management?

So what is master data management and what is a true cloud-native MDM? Cloud-native is a phrase tossed around a lot these days. It is the modern approach to building applications using continuous integration on immutable infrastructure packaged in containers on serverless or managed services deployed using microservices.
The obvious question arises – why? Why is the cloud-native master data management model gaining popularity? And why is it considered better than the on-premise, hosted, or hybrid model?
While architecture and technology provide operational flexibility, the business benefits of cloud-native models are more wide-ranging.
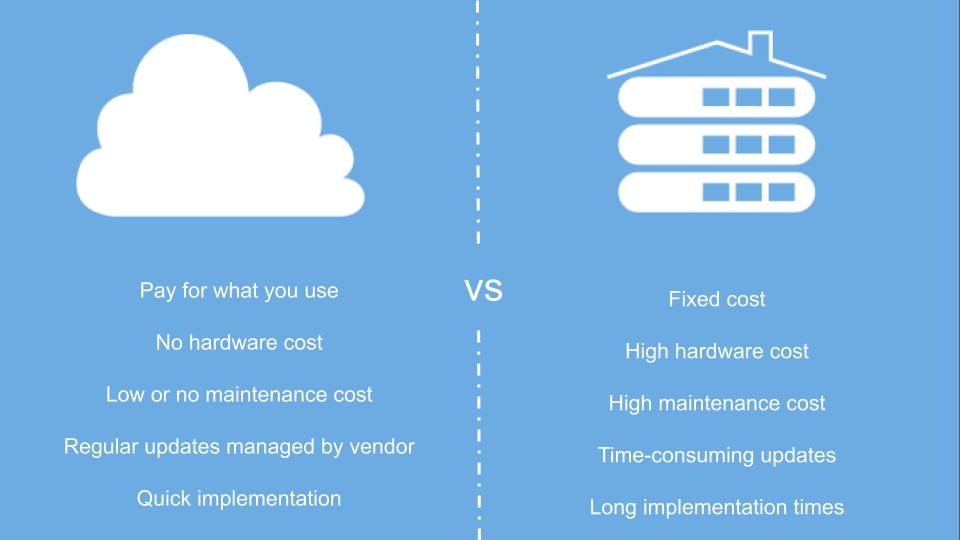
- Responsive businesses can adapt faster to changing business needs, benefiting from the flexible microservices architecture, easy upgrades, seamless scaling, as well as quick portability the cloud provides.
- Get up and running with lower effort and benefit from the best practices of other enterprise and business users, businesses achieve faster time-to-value for all stakeholders.
- No staff of IT professionals is required to manage the infrastructure further lowering the TCO.
- Lower Capex coupled with higher scalability, portability, and redundancy offer businesses a much lower Total Cost of Ownership.
Advantages of Cloud vs On-Prem
In the Hype Cycle for Cloud Computing, 2019, Gartner noted that cloud-native is on the rise. While it affirms that technology is here to stay, not all cloud-native labels are the same.
Cloud-native MDM tool (Master Data Management) is expected to adopt the unique features of the cloud to deliver exceptional versatility and elasticity – embedded in responsive data management. Some MDM system platforms carrying the tag may just be offering a cloud-ready or hosted model that has been force-fitted to run in the cloud. However, they do not have the innate flexibility that comes with a born-in-the-cloud master data management solution.
What are the various Master Data Management delivery models?
Let’s first take a look at various Master Data Management delivery models available in the market
On-premise
The on-premise MDM model is the legacy enterprise software delivery model that we see installed locally on a customer’s infrastructure (servers, databases, OS). Monitoring, operating, backups, redundancy, failovers as well as upgrading the master data management software and hardware are the responsibility of the customer. The on-premise model comes with a substantial Capex commitment and also claims a significant Opex. Security, scaling, and business continuity are fully managed by the customer.
Cloud-hosted
Running on-premise MDM platform with a cloud provider is, for some companies, a shortcut to claiming that they have a cloud-based MDM. As the underlying architecture is the same as the on-premise version, they cannot leverage the benefits of cloud services. Cloud-hosted MDM is still challenging to upgrade and requires manual effort and considerable investment to manage the migrations. Monitoring and maintenance of the hosting account are often the responsibility of the customer, reducing the benefits of being in the cloud.
Cloud-native
Cloud-native MDM is built from the ground up to run on cloud infrastructure and services. Designed exclusively for the cloud, it can easily provision seamless upgrades and release cycles. In more modern cloud-native offerings, capabilities are broken into smaller components called microservices, the release cycles are faster without disruption to the business.
Leveraging native cloud monitoring and alerting to improve service levels helps a cloud-native MDM solution meet much improved SLAs over on-premise and cloud-hosted MDM. Scaling to meet growing business demands to handle peak capacity and varying performance requirements while managing infrastructure costs is a significant advantage and provides the best dollar value.
Provider-native
Provider-native MDM is Cloud-native MDM taken a step further to take advantage of provider-specific capabilities, improving reliability, availability, scalability, and performance. Provider-specific capabilities including managed services run only on a single cloud provider. The application is developed on a public cloud provider’s stack and the cloud provider efficiently monitors, upgrades, and operationalizes the service.
When it comes to the lowest total cost of ownership, cloud-native and provider-native MDM surpasses the other models. The Data Management Buyers Guide establishes that cloud-native subscriptions offer net cash flow savings of 30-50% over non-subscription, hosted, or on-premise deployments. With a detailed comparison of data platform models, it concludes that operationally and financially, the cloud is the optimal approach for the vast majority of workloads.
The Difference in Architecture and Technology
Master Data Management models have evolved over time to address diverse organizational data management challenges. To maximize the business value from your MDM, you need a flexible architecture and the matching technology supporting business agility and build in responsiveness. Let’s consider how architecture and technology vary across the models.
NoSQL database technology
A critical element in building a cloud-native solution because of its horizontally scalable nature, typical examples of NoSQL databases are Cassandra, MongoDB, AWS DynamoDB, and Google BigTable.
NoSQL database technology enables horizontal scalability to add extra capacity when customer data workloads increase quickly. Helping scale to handle any volume of master data, this technology fully supports ingesting interaction data as well.
Multi-model Data Management
Cloud-native MDM leverages multi-model data management to support both operational and analytic use cases. This provides agility to allow purpose-built services and components that can be used together to provide an enhanced customer experience for any use case.
Locking into a specific data integration and storage model of a non-cloud MDM strategy may prove to constrain over time, as the changing business needs start demanding more flexible and comprehensive architecture.
Availability of managed services
Managed services are provider-specific services that take away the need to manage infrastructure and components so you can focus on core activities – your business process. In addition to improving operations and lowering the total cost of ownership for cloud-native MDM software, managed services offer you better time-to-value.
In comparison, other ‘engineered cloud offerings’ cannot keep up in efficiency as they struggle with high costs of taking on the responsibility of operationalizing all services.
Auto-scaling
The Scalability Imperative: Responsiveness to Manage Planned and Unplanned Spikes elaborates on how scalability and responsiveness are imperative to deliver optimized, hyper-personalized experiences that today’s market demands. Cloud-native MDM automatically responds to spikes in usage and auto-scales based on utilization for most layers of the platform. Auto-scaling supports setting limits to protect customers from runaway or unexpected costs.
The other models instead add capacity the old way and have trouble competing in terms of responsiveness.
Going cloud-native is not just moving your MDM to cloud, but moving to a new paradigm of totally transformed underlying architecture and technology.
The True Cloud-Native Master Data Management
True cloud-native MDM architecture is designed fundamentally for cloud and is ‘born-in-the-cloud’. It utilizes some of the most cutting-edge technologies and services available today. In comparison to other models, only true cloud-native MDM is able to leverage these capabilities to deliver superior business benefits.
For example, Reltio Connected Customer 360, a true cloud-native SaaS platform leverages managed services to deliver high business agility. Reltio is able to deliver a highly reliable and efficient service to its customers because of its partnership with cloud providers like AWS and GCP. Reltio takes advantage of managed services like AWS DynamoDB, Google BigTable, and Google BigQuery. AWS and GCP heavily invest in the development of these services ensuring that automatic upgrades of infrastructure and services occur regularly and without impact on customers.
With multi-model support, you can easily onboard diverse data sources from multiple systems and efficiently handle both analytical as well as operational use cases. Operational use cases are run through a dedicated search service purpose-built to provide results with low latency. Analytic use cases, on the other hand, are run through Reltio Data Science or Reltio Analytics and use technologies like Spark, Qubole, S3, GCS, and BigQuery. Purpose-driven services with storage layers built to accommodate access patterns ensure rapid response to changing business requirements.
Taking advantage of autoscaling, Reltio effortlessly scales to manage demand spikes at business speed for responsive businesses. The ability to provide large volumes of trusted and critical data at scale to downstream systems for real-time decisions makes a true cloud-native responsive data management platform an obvious choice for business agility.
Watch the webinar on how Reltio Connected Customer 360, a true cloud-native platform can help your business adapt faster to changing business needs, with a lower TCO and faster time-to-value.

