Master Data vs Reference Data: Data Type Comparison

The difference between master data vs reference data seems simple enough based on definitions. Most will tell you that reference data is a subset of master data, and it is, sort of.
- Master Data: The information that you share across your enterprise to analyze and drive business processes for operational efficiency.
- Reference Data: Stable and widely used data that categorizes master data and correlates it with external data standards.
All organizations have enterprise data on their products, assets, financials, employees, and customers, but where this data is housed can range from siloed databases to spreadsheets to old file cabinets. Bringing the data sources together in an actionable format accessible across the enterprise — with consistent definitions and organization — creates master data. And multi-domain, cloud-native master data management (MDM) powers your ability to gain insights from that data.
There are two kinds of reference data, as you can note from the definition: external and internal. External reference data includes rarely changing norms like countries, currencies, languages, and units of measure. Internal reference data is where it gets complicated. It defines and structures master data, mapping it to your business processes. Internal reference data exists to turn other data into business information.
Examples of Master Data
To dig a little deeper into master data vs reference data in context, let’s take a step back and look at the most common examples of master data.
- Customer: customer profiles, where they shop, how they buy, what they buy. When a customer buys a product from your website after clicking on a link in a social media ad, the data on the social media site, customer profile, product, and ad all contribute to master data.
- Financial: asset management policies, accounting groups, financial regulations, and financial account hierarchies. All the nooks and crannies of where your business spends money as well as each expenditure’s ROI.
- Governance: data supporting privacy and industry-specific regulations and the guardrails defining where the compliance team steps in.
- Location: where your businesses have offices, stores, and suppliers and where your customers live.
- Employee: data on how many you have, their salaries, roles, and hierarchy.
- Product: product descriptions, inventory, the parts, and production supply chain, and the stores and distribution centers carrying it. When there’s a product recall because of a flaw or contamination at a specific supplier, which products have parts from that supplier and which locations they’re at are all elements of master data.
Types of Data
To see master vs reference data in the full context of the master data environment, it might also help to zoom out and look at various types of data.
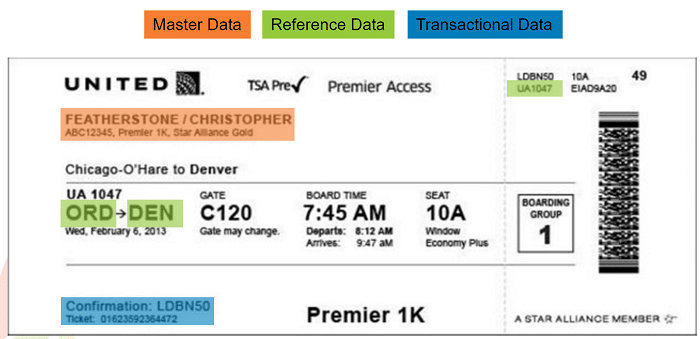
Transactional
Transactional data includes data on business events like purchases from suppliers, sales to customers, invoices, returns, customer help tickets, deliveries, and employee hires. Transactional data is the everyday, operational information in your CRM, ERP, and HR databases.
Metadata
This is the data that describes your data, like descriptions in databases, configuration files, and log files. A great way to conceptualize metadata is to think of the information in the popup when you right-click a closed file to “Get Information.”
Reference Data
Reference data is data that’s used for categorizing master data or relating to information outside your business, like customer segments, business processes, countries, and zip codes. Reference Data is a non-volatile and slow moving subset of master data.
Unstructured Data
This includes data from social media posts, emails, white papers, or help chats that is difficult to categorize. Often it ends up as part of Big Data.
Big Data
Big data is a bit of a buzzword, but leveraging it is key to winning in the experience economy. What makes data ‘big’ is that the volume, variety, and/or velocity outstrip traditional technologies, and it requires machine learning and AI to derive insights. If Big Data isn’t part of your master data management platform now, you should be developing a plan to include it in the near future.
A key element of master data governance means qualifying what data sources and data types should be included in the MDM platform to provide the most valuable insights to power business goals. Enter reference data. Internal reference data defines the types of data (and minute segments from those types of data) that are key to your business processes. Reference data also provides a base for mapping relationships between data and how an MDM provides insight ready data.
Is reference data master data?
So, with all that context, master data vs reference data becomes a bit cloudy. Reference data is a subset of master data, but it’s more than that. Some people describe reference data as the master of master data.
Really, internal reference data is the information that gives your MDM platform the structure to power every business process. It’s the taxonomies and hierarchies of data that reveal relationships in your master data.
When thinking about how master data vs reference data relate to business process, consider:
- Master data: changes are part of the business model (like adding new customers and products)
- Reference data: changes constitute a transformation in business processes (like new product category or business function)
What is a reference data model?
Understanding master data vs reference data may at first seem like a technical question specific to IT personnel. But reference data are the building blocks of your reference data model, which represents the content, relationships, and constraints needed for your MDM platform to produce the desired insights. Mapping a reference data model requires human judgment, and when the reference data powers business logic and business processes like segmenting customer data, that judgment is beyond IT’s scope.
Executives from across the organization need to help software architects understand what they want the data to do and what kinds of drivers and trends they want to be able to see. They ensure that the reference data model reflects your business norms and that entities and relationships in the reference data model mirror the objects and operations in your organization.
How do you manage reference data?
It’s rare that business executives get involved in developing reference data, and the result means obscurity about the specific governance and needs for proper reference data management.
Until recently, businesses have been mostly on their own to build reference data rules and execute the tasks to make sure data adheres to them. This looks a lot like the kind of mess at hand before master data management came along: hundreds of reference data files or spreadsheets with infrequent and uncoordinated manual updates.
Reference data shouldn’t change often, but when it does it sends ripples across every function in the enterprise. Proper reference data management occurs centrally in coordination with the data governance team stewarding the full MDM platform.
The reference data management team needs to track both internal and external reference data, assuring:
- External reference data: APIs connect the reference data to external regulatory authorities like government agencies or currency converters. Incoming data gets sorted and selected to align with established master data.
- Internal reference data: Definitions and categories remain relevant to current business processes and serve the needs of all business disciplines. Ensure data stewards remain consistent in reference data creation and management.
Proper reference data management promotes agility in the MDM platform. When business processes change, it’s easy to see in the reference data model where to add in new codes without completely restructuring your MDM. If you need to categorize your master data differently for a new analytical application or add a short-term code for marketing promotion, you need an MDM solution that can adapt easily to power real-time operations at scale.
The Cost of Poor Reference Data Management
By contrast, poor reference data management(RDM) can mean enterprises are making business decisions based on disjointed data and missing connections between data that power business transformation. Bad RDM costs more to manage, causes delays in launching new applications, and makes systems prone to failure. It affects both operational and analytical MDM.
Poor RDM in Operational MDMs:
- Invalid transactions
- Transaction failure across multiple systems, poor efficiency of downstream transactions
- Compliance risk (e.g. improper tax codes)
- Inability to build custom hierarchies for reference data
- Difficult to manage internationalization and global harmonization
Poor RDM in Analytical MDMs:
- Errors in reference data affect master data quality
- Multiple versions of reference data
- No clear visibility into reference data usage
- No easy way to change and update reference data across multiple systems
- No central review and approval governance
- Challenges synchronizing and versioning
The Reltio platform includes reference data management as a part of its MDM at no additional charge. It translates external data to reference data during imports and export and helps create, update, and version control internal reference data. It includes crosswalks to help data stewards understand the impact of data changes and audit trails on all workflows.
At Reltio, we understand the difference between master data vs reference data and that multi-domain, cloud-native MDM needs excellent RDM to custom fit to your business needs and power your customer-centric business.
Related Content:
